Distinguishing between DRC tube-type and tubeless tires – understanding them correctly to make the right choice for your vehicle – is an essential step that helps users select the product that best suits their operating needs, terrain conditions, and desired level of safety. Each tire type has its own structure, advantages, and performance characteristics, requiring users to fully understand them before choosing the right tire for motorcycles, electric bikes, or motorbikes. The following article will analyze in detail the construction, operating mechanism, advantages disadvantages, and real-world applications of each DRC tire type, giving you a comprehensive and accurate perspective.
1. Overview of the Two DRC Tire Types: Tube Type (TT) and Tubeless (TL)
DRC is one of the leading tire brands in Vietnam and Southeast Asia, with the widest coverage in the motorcycle and commercial vehicle tire segments. Its product lines include:
- Tube-Type (TT): Used in combination with an inner tube made of rubber.
- Tubeless (TL): Does not require an inner tube; air is retained thanks to the airtight rubber layer inside the tire.
Choosing the right tire type not only affects the riding experience but also impacts safety, tire lifespan, and long-term operating costs.
2. Structure of DRC Tube-Type and Tubeless Tires – Core Differences
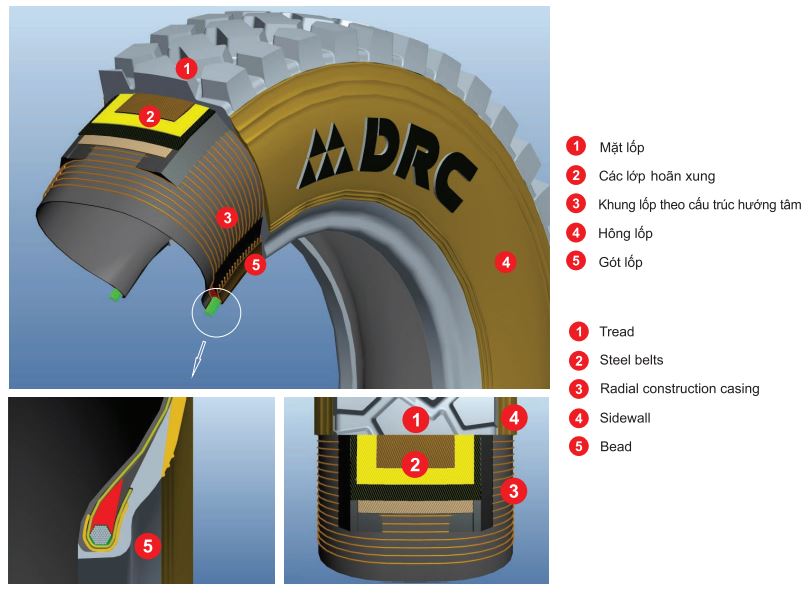
2.1. Structure of DRC Tube-Type Tires (Tube Type – TT)
Tube-type tires consist of two main components:
- Tire (outer casing): Constructed from nylon ply layers, natural rubber + synthetic rubber, and tread patterns depending on the design.
- Tube (inner tube): Made from butyl rubber, containing a valve to hold air and maintain internal pressure.
Structural characteristics of DRC TT tires:
- Thinner sidewalls compared to tubeless tires.
- Low airtightness requirement because the tube performs that function.
- The rim does not need a tubeless-compatible design.
2.2. Structure of DRC Tubeless Tires (Tubeless – TL)
Tubeless tires are engineered with a more modern and optimized structure, featuring:
- Airtight liner: Replacing the role of the inner tube, made from premium butyl rubber.
- Thicker, stronger sidewalls for improved puncture resistance.
- Specialized bead design that seals tightly against the rim to retain air without a tube.
- TL tires require a rim specifically designed for tubeless use.
3. Operating Mechanism – Why Tube-Type and Tubeless Tires Behave Differently
3.1. DRC Tube-Type Tires – Traditional Mechanism
When inflated, pressure is held inside the tube—not the tire casing. The tube presses against the inner surface of the tire, making the tire firm and helping it grip the rim.
Disadvantages of this mechanism:
- When punctured, the tube loses air rapidly → sudden deflation.
- Tubes can be pinched or twisted during installation.
- Friction between tube and tire generates heat → higher risk of blowouts at high speed.
3.2. DRC Tubeless Tires – Modern and Safer Mechanism
Tubeless tires operate based on:
- Air being contained directly inside the tire thanks to the airtight liner.
- Air escapes slowly when punctured → reduces the risk of sudden collapse.
- Small holes can be temporarily sealed using sealant or a repair kit.
This mechanism enhances stability and safety during operation.
4. Advantages – Disadvantages of DRC Tube-Type and Tubeless Tires
4.1. Advantages of DRC Tube-Type Tires
- Lower cost, suitable for common commuter bikes.
- Easy to repair by replacing the tube.
- No need for a tubeless-type rim.
- Suitable for older vehicles without tubeless support.
4.2. Disadvantages of Tube-Type Tires
- Prone to tube pinching and rapid air loss.
- Sudden deflation when punctured.
- High heat generation on long or heavy-load trips.
- Lower load capacity compared to tubeless tires.
4.3. Advantages of DRC Tubeless Tires
- High safety: slow air loss when punctured.
- Can self-seal small holes.
- Strong sidewalls → excellent load capacity.
- Less heat buildup at high speeds → longer lifespan.
- Better road grip, especially when cornering.
- Lighter overall weight → improved fuel efficiency.
4.4. Disadvantages of Tubeless Tires
- Higher price.
- Requires tubeless-compatible rim.
- Bigger punctures require specialized tools to repair.
5. Detailed Comparison Between DRC Tube-Type and Tubeless Tires
5.1. Load Capacity
| Tire Type | Load Capacity |
| DRC Tube-Type | Average |
| DRC Tubeless | 10–20% higher |
5.2. Safety
- Tube-Type: prone to sudden flat → dangerous at high speed.
- Tubeless: slow air leakage → easier to control.
5.3. Long-Distance Travel
- TL tires generate less heat → more durable for long trips.
- TT tires suit short to medium distances.
5.4. Road Grip
- Tubeless tires offer superior grip thanks to modern tread design.
5.5. Repairability
- TT: quick, cheap tube replacement.
- TL: more difficult if severely punctured.
6. Real-World Application – Which Tire Should You Choose?
6.1. Popular Manual Motorbikes (Wave, Sirius, Future…)
- Short local trips: Tube-Type is economical.
- Daily commuting or high-speed riding: DRC DPLUS Tubeless is better.
6.2. Scooters (Vision, Air Blade, Lead, SH)
- Most scooters use tubeless tires for safety and stability.
- DPLUS popular sizes: 80/90-14, 90/90-14, 110/80-14…
6.3. Electric Motorbikes
- Tubeless tires perform better: high load capacity, strong grip, ideal for short urban travel.
7. Key DRC Product Lines in Both Segments
7.1. DRC Tube-Type Tires (TT)
- DRC TT Series (sizes 2.25–17, 2.50–17…)
- Fine and coarse tread options for rough terrain
- Suitable for daily commuting and service vehicles
7.2. DRC Tubeless Tires (TL) – DPLUS
- DPLUS scooter tires
- DPLUS tubeless tires for manual bikes
- DPLUS electric-bike tires
- Anti-wear technology – enhanced durability
- Thick sidewalls – puncture resistant
- Excellent load performance
8. How DRC Controls Tire Quality
8.1. Strict Selection of Raw Materials
- Vietnamese natural rubber
- High-grade synthetic rubber (SBR, BR)
- Reinforcing and anti-oxidation additives
8.2. Optimized Mixing – Extrusion – Building Process
Ensures strong structure, high uniformity, and reduced deformation during operation.
8.3. Automated Inspection and Rigorous Testing
- Load test
- Burst pressure test
- Abrasion test
- X-ray inspection for radial tire lines (international standards)
9. Common Mistakes When Choosing Tube-Type or Tubeless Tires
- Thinking all bikes can use tubeless tires.
- Using tubeless tires on non-tubeless rims → air leakage.
- Choosing the wrong size → faster wear or higher fuel consumption.
- Not checking air pressure regularly.
- Using low-quality tubes → risk of blowout.
10. Expert Advice from DRC – Which Tire Is Right for You?
- Prioritizing safety, durability, daily city riding
→ Choose DRC DPLUS tubeless. - Older bikes, non-tubeless rims, cost-saving needs
→ Choose standard DRC tube-type tires. - Frequent long-distance or high-speed riding
→ Tubeless is the optimal choice. - Rough roads, heavy loads, service vehicles
→ Tubeless recommended for better heat resistance and load capacity.
Distinguishing between DRC Tube-Type and Tubeless tires – understanding them correctly to choose the right one – plays a crucial role in optimizing safety, reducing costs, and extending tire lifespan. Each tire type has its own advantages, suitable for specific usage conditions and vehicle types. With decades of experience, DRC provides a full range of high-quality tires for both segments, meeting strict technical standards and Vietnam’s diverse road conditions.
Read more: How to Extend Truck Tire Lifespan: Expert-Proven Tips